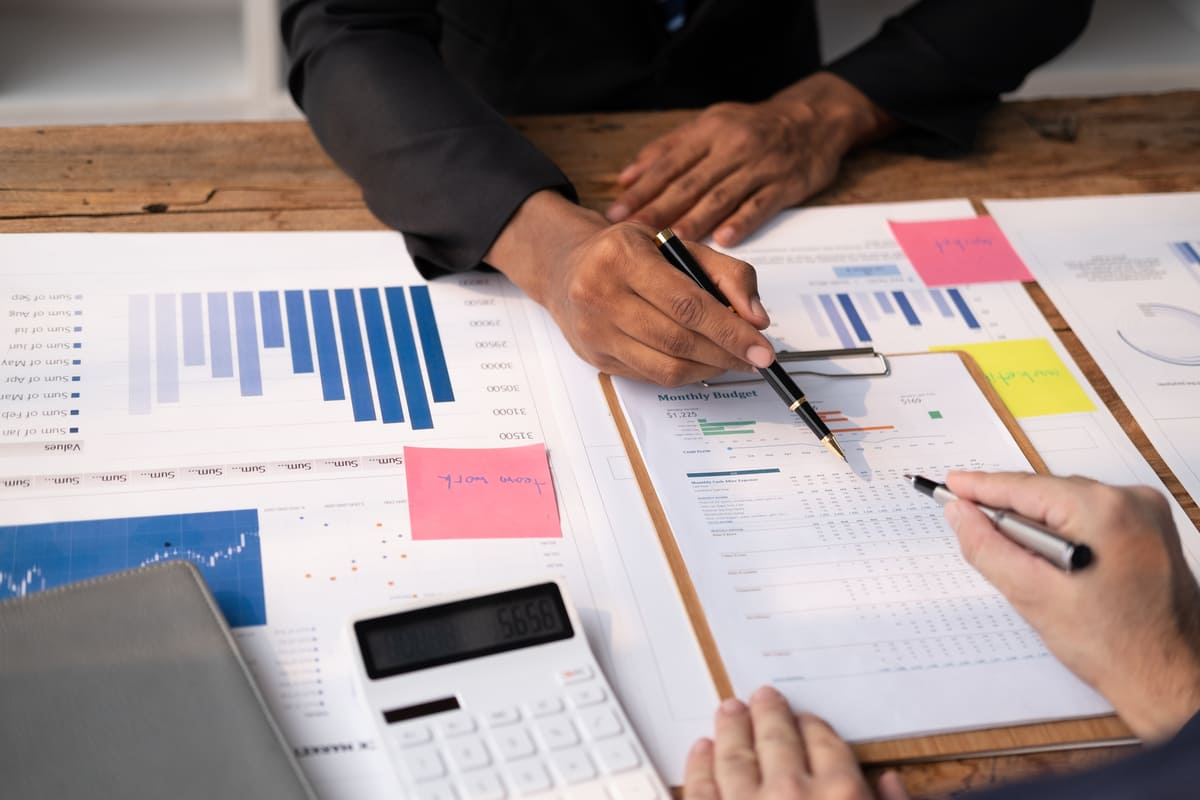
The world of accounting is constantly evolving, and one of the most significant changes in recent years has been the introduction of the 606 accounting standard.
Officially known as the Revenue from Contracts with Customers standard, ASC 606 has fundamentally transformed how companies recognize revenue.
This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive and detailed guide to mastering the 606 accounting standard, offering insights into its principles, implementation, and impact on businesses.
What is the 606 Accounting Standard?
The 606 accounting standard, also known as ASC 606, was introduced by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) to create a unified model for revenue recognition across industries and geographic boundaries.
ASC 606 replaces several previous standards, including ASC 605, which led to inconsistencies and complexities in revenue recognition practices.
Objectives of ASC 606
The primary objectives of ASC 606 are to:
- Standardize revenue recognition practices across various industries.
- Enhance comparability of financial statements.
- Improve disclosure requirements, providing better insights into revenue streams and business performance.
Importance of Revenue Recognition
Revenue recognition is a critical aspect of financial reporting because it directly impacts a company’s financial health and performance.
Accurate revenue recognition ensures that financial statements reflect the true economic activities of a business, providing stakeholders with reliable information for decision-making.
Core Principles of 606 Accounting
ASC 606 is built around a five-step model designed to streamline the process of recognizing revenue from contracts with customers. Let’s explore these steps in detail:
Identify the Contract with a Customer
A contract is an agreement between two or more parties that creates enforceable rights and obligations. Under ASC 606, a contract must meet the following criteria:
- The contract has been approved by all parties involved.
- The rights and obligations of each party can be identified.
- Payment terms are clear.
- The contract has commercial substance.
- It is probable that the entity will collect the consideration to which it is entitled.
Identify the Performance Obligations in the Contract
Performance obligations are distinct goods or services that a company promises to deliver to a customer. A good or service is distinct if:
- The customer can benefit from the good or service on its own or together with other resources readily available.
- The promise to transfer the good or service is separately identifiable from other promises in the contract.
Determine the Transaction Price – 606 Accounting
The transaction price is the amount of consideration a company expects to receive in exchange for transferring goods or services to a customer. This amount can be fixed, variable, or a combination of both. Factors to consider when determining the transaction price include:
- Variable considerations and constraints
- Significant financing components
- Non-cash consideration
- Consideration payable to a customer
Allocate the Transaction Price to the Performance Obligations
Once the transaction price is determined, it must be allocated to the performance obligations identified in the contract.
This allocation is generally based on the standalone selling prices of the distinct goods or services. If standalone selling prices are not readily observable, they must be estimated using appropriate methods such as:
- Adjusted market assessment approach
- Expected cost plus a margin approach
- Residual approach
Recognize Revenue When (or As) the Entity Satisfies a Performance Obligation
Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to the customer.
Control can be transferred either over time or at a point in time. To determine the timing of revenue recognition, companies must consider:
- The nature of the performance obligations
- Transfer of control indicators, such as the customer having a legal title, physical possession, or significant risks and rewards of ownership.
Implementation Challenges and Strategies
Challenges in Implementing 606 Accounting
Complex Contracts
Contracts with multiple performance obligations or variable consideration components can be challenging to analyze and allocate appropriately.
Changes in Business Practices – 606 Accounting
Businesses may need to adjust their processes and systems to comply with ASC 606, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Enhanced Disclosure Requirements
ASC 606 requires more detailed disclosures, which means companies need to collect and report additional information.
Strategies for Successful Implementation
Comprehensive Training
Ensure that all relevant personnel are adequately trained on the new standard and its implications for revenue recognition and financial reporting.
Robust Systems and Processes
Implement robust systems and processes to handle the complexities of ASC 606, including the ability to track performance obligations, allocate transaction prices, and manage variable consideration.
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Regularly monitor and review contracts, revenue recognition practices, and disclosure requirements to ensure ongoing compliance with ASC 606.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Technology Sector
In the technology sector, contracts often include multiple performance obligations, such as hardware, software, and services. Companies must carefully evaluate whether these components are distinct and allocate the transaction price accordingly.
Construction Industry – 606 Accounting
For construction contracts, revenue is often recognized over time as the project progresses. Companies must assess the extent to which the customer controls the asset being constructed and whether they have an enforceable right to payment for performance completed to date.
Healthcare Industry
Healthcare providers may face challenges in recognizing revenue from patient services, particularly when dealing with insurance reimbursements and variable consideration related to patient outcomes and performance metrics.
Licensing and Franchising
Licensing and franchising arrangements often involve variable consideration and complex performance obligations. Companies need to carefully evaluate the terms of the contract and apply the appropriate revenue recognition principles.
Comparison with ASC 605
ASC 606 introduces a more structured and comprehensive framework compared to ASC 605, which was often criticized for its industry-specific guidance and lack of consistency. Key differences include:
- ASC 606 provides a single, principles-based model for revenue recognition, applicable across all industries.
- It emphasizes the identification of performance obligations and allocation of transaction prices based on standalone selling prices.
- Enhanced disclosure requirements under ASC 606 provide more transparency into revenue streams and business performance.
Benefits of the New ASC 606
Consistency and Comparability
A unified model improves consistency and comparability across industries and geographical regions.
Transparency – 606 Accounting
Enhanced disclosure requirements provide stakeholders with better insights into a company’s revenue recognition practices and financial health.
Flexibility
ASC 606 allows for greater judgment and flexibility in accounting for complex revenue arrangements.
Enhanced Disclosure Requirements – 606 Accounting
Disaggregated Revenue
ASC 606 requires companies to disclose revenue disaggregated by categories that depict how the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factors. This may include disaggregation by:
- Type of good or service
- Geographical region
- Market or customer type
- Contract duration
Contract Balances
Companies must disclose information about contract balances, including:
- Contract assets and liabilities
- The amount of revenue recognized in the reporting period that was included in the contract liability balance at the beginning of the period
- Significant changes in contract balances during the period
Performance Obligations – 606 Accounting
Disclosures related to performance obligations include:
- When the company typically satisfies its performance obligations
- Significant payment terms
- The nature of the goods or services that the company has promised to transfer
- Obligations for returns, refunds, and other similar obligations
Transaction Price Allocation
Companies need to disclose:
Methods used to allocate the transaction price to performance obligations
Information about estimating variable consideration
Adjustments for significant financing components
606 Accounting ASC – Concluding Remarks
The 606 accounting standard represents a significant shift in how companies recognize revenue, bringing greater consistency, transparency, and comparability to financial reporting. Mastering ASC 606 involves understanding its core principles, implementing effective systems and processes, and continually monitoring and adjusting practices to ensure compliance. By doing so, companies can provide more reliable financial information to stakeholders, ultimately supporting better decision-making and enhancing overall business performance.
Adopting ASC 606 may present challenges, but with comprehensive training, robust systems, and a clear understanding of its principles, businesses can successfully navigate this new landscape and reap the benefits of improved revenue recognition practices.